If you’ve called a customer service line or used a chatbot on a business’ website or social media page, then chances are you have probably interacted with conversational AI (CAI).
Conversational AI has seen a rapid rise in usage in a short period of time. Although forms of this tech existed prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, interest boomed when it proved to be a helpful solution to the unique pressures and changes businesses were facing, especially as it provided a cost-effective way for brands to offer customers 24-hour assistance.
By the end of this blog, you’ll have an understanding of:
- What is conversational AI?
- How is conversational AI used for enterprises?
- How to build a conversational AI strategy for the future
What is conversational AI?
CAI refers to technologies that people can talk to, like chatbots or virtual assistants. These iterations use a combination of machine learning, natural language processing, and large amounts of data in order to replicate human interactions and understand text across various languages.
In short, conversational AI facilitates human-like discussions between a human and a computer in real-time. However, there are a few misconceptions surrounding conversational AI that should be noted.
Conversational AI isn’t one, single thing
While each AI model is in charge of a specific task, AI refers to a system of engines that work together for larger automation. Similarly, conversational AI is a combination of different technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and contextual awareness.
Not all chatbots are created equal
Not to be confused with the first forms of chatbots, conversational bots that are infused with AI offer life-like communications and can recognize speech, text, and different languages while understanding intent and how to respond in a way that mimics human conversation.
Conversational AI is as helpful as a human representative
While there are certain interactions that can’t be automated yet, virtual assistants and chatbots are great for answering queries and performing simple tasks. Businesses may be concerned with how this could affect customer experience, but nearly 40% of global internet users say they prefer interacting with chatbots.
How can enterprises use conversational AI?
As mentioned before, one of the most common iterations of CAI in business is the use of virtual assistants, particularly for customer support, since it allows the brand to create one-on-one interactions around the clock and in several languages.
With its ability to create more helpful and more meaningful conversations with customers while being more cost- and time-effective than traditional methods, it’s easy to see why large-scale businesses have implemented the use of CAI.
For example, when Meta (FKA Facebook) Messenger introduced special automated chats for businesses, the number of chatbots in Messenger grew from 100K in 2017 to 300K in 2018. Most recent reports from Messenger share that over 40M global firms are active on Messenger and putting conversational commerce to use.
There continue to be opportunities for growth. Business Insider Intelligence predicts that by 2024, worldwide consumer retail spend via chatbots will reach $142B, surpassing 2019’s $2.8B. And a study by Juniper Research expects that CAI could save businesses and consumers over 2.5B customer service hours by 2023, coming out to an annual $11B in business cost savings across the retail, finance, and healthcare sectors.
While conversational AI platforms for larger brands are most commonly used via enterprise chatbots and virtual assistants, there are many other potential use cases. With the right tools and applications, enterprise businesses can target multiple roles for automation.
The following highlights some of the use cases for CAI:
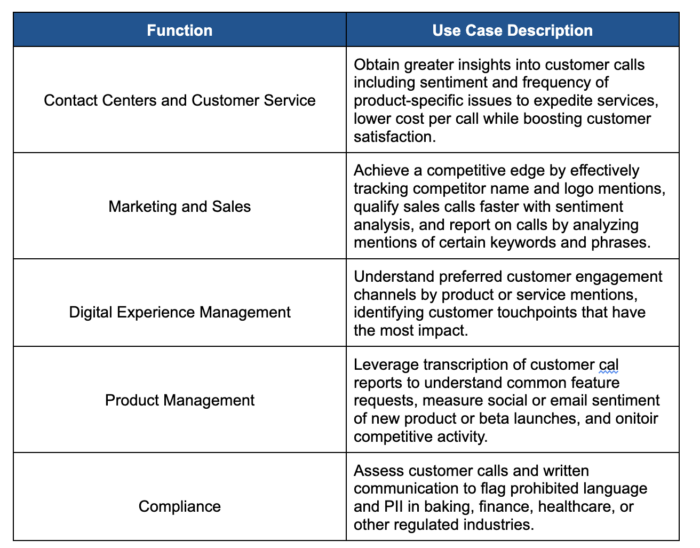
Synthetic Media and Conversational AI
With the advent of synthetic media including voice cloning and 3D avatar creation, CAI is in the midst of another evolution. Leveraging artificial intelligence to create realistic sounding voices of paid actors and well-known talent (with their expressed approval), as well as stock and custom avatars, CAI digital interactions will leverage avatars with realistic voices that customers can interact with to obtain answers, schedule appointments, and much more. With AI-powered applications such as Veritone Avatar and Veritone Voice, companies can access an ethical, cost-effective, and truly digital way of creating custom avatars and synthetic voice to bring CAI experiences to life.
How to build a conversational AI strategy for the future
Before implementing a conversational AI practice, you should consider these checklist items to align your strategy with your current business needs.
- Identify your business goals: Before building the bot, be sure to clarify and stay true to the business’ goals and key initiatives.
- Consider compliance and data privacy: Even if your original use case may not require compliance and data privacy, making it a part of your CAI practice from the start will create fewer headaches down the road.
- Understand your customers: If you’re using CAI to interact with your customers, understanding them is the key to creating lifelike conversations and anticipating their needs.
- Maximize value with compatibility and integrations: Integrate your CAI with all channels your customers (or team members) will be interacting with to avoid forcing the user to switch between channels or wait for a live agent to help.
- Find the right partners: Implementing any AI related technology is no easy task, so finding a partner with the right solutions, like Veritone, can help meet your enterprise’s current and future needs.
Implementing AI no matter the use case requires foundational technology that can scale as the business evolves. An Enterprise AI platform plays a crucial role in establishing an organizational-wide AI practice. In the next blog, we’ll provide an overview of Enterprise AI platforms to help you streamline your AI technology implementation.





